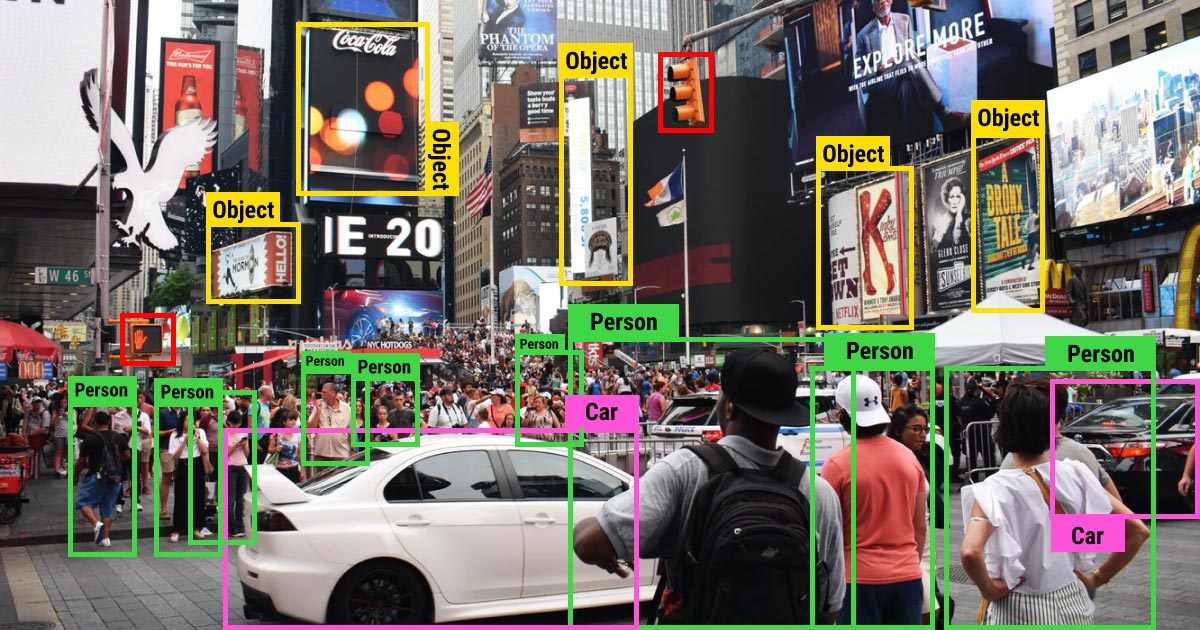
In today’s digital age, where images are shared and consumed at an unprecedented rate, the need for efficient and accurate image recognition technologies has become paramount. Image recognition, a branch of computer vision, enables machines to interpret and understand visual data, mimicking the human ability to recognize objects, patterns, and faces. This revolutionary technology has vast implications across various industries, from autonomous vehicles and surveillance systems to e-commerce and healthcare. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of image recognition, its applications, challenges, and the promising future it holds.
Understanding Image Recognition
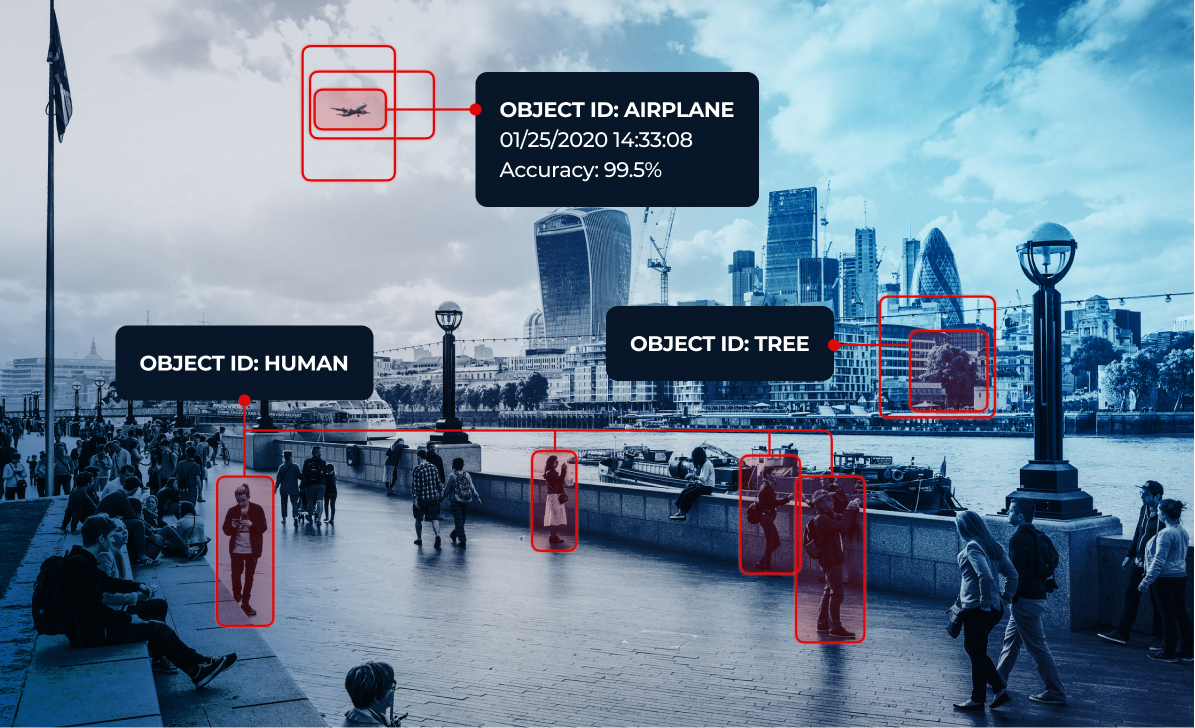
Image recognition, also known as image classification, is a field of study that involves teaching machines to understand and interpret visual information. By utilizing complex algorithms and deep learning techniques, image recognition systems can identify objects, scenes, and patterns within images or video frames. This technology has advanced significantly in recent years, thanks to the rapid development of artificial intelligence and neural networks.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in image recognition. Through deep learning algorithms, AI models can extract meaningful features from images and make predictions based on the patterns it learns from vast amounts of training data. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool in image recognition, enabling the detection of intricate patterns and complex visual structures.
Key Components of Image Recognition
To understand the image recognition process, we must delve into its key components:
1. Image Acquisition
The first step in image recognition is acquiring images from various sources such as cameras, satellites, or databases. These images serve as the input data for subsequent processing.
2. Preprocessing
Preprocessing involves enhancing the acquired images by removing noise, adjusting brightness and contrast, and resizing them to a standardized format. This step ensures the images are in a suitable condition for accurate analysis.
3. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction involves extracting relevant visual features from the preprocessed images. These features can include edges, corners, textures, or more abstract features specific to the objects being recognized.
4. Classification
In the classification stage, the extracted features are fed into a trained model works that assigns labels or categories to the images. The model training learns from labeled training data and generalizes its knowledge to accurately classify unseen images.
Applications of Image Recognition
Image recognition technology has a wide range of applications across various industries. Let’s explore some of its prominent use cases:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Image detection is vital for the development of self-driving cars. By analyzing visual input from cameras and sensors, autonomous vehicles can detect objects, pedestrians, traffic signs, and lane markings, enabling them to make informed decisions and navigate safely.
2. Healthcare and Diagnostics
In the healthcare industry, image object detection is revolutionizing diagnostics. By analyzing medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, image detection algorithms can assist doctors in detecting abnormalities, tumors, or other medical conditions, leading to more accurate diagnoses and timely interventions.
3. Security and Surveillance
Image detection plays a crucial role in security and surveillance systems. It enables real-time monitoring and analysis of video feeds, detecting suspicious activities, identifying individuals, and enhancing overall situational awareness.
4. E-commerce and Visual Search
E-commerce platforms are leveraging image detection to enhance the shopping experience. Visual search allows users to find products by uploading images, enabling them to search for similar items based on shape, color, or pattern. This technology simplifies product discovery and increases customer engagement.
5. Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) applications heavily rely on image recognition to overlay virtual content onto the real world. By recognizing and tracking objects or markers in real time, AR systems create immersive and interactive experiences, merging the physical and digital realms.
Case Studies with Record-Breaking Achievements
1. Tesla’s Autonomous Driving System

Tesla’s self-driving technology is a prime example of image recognition’s potential. By using a suite of cameras and image recognition algorithms, Tesla’s vehicles can navigate complex environments and achieve remarkable levels of autonomy. This technology has set new records in autonomous driving and continues to evolve.
2. Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo

Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo utilized advanced image recognition techniques to analyze the game board and make strategic moves, defeating world champion Go players. This achievement showcased the power of image recognition in understanding and processing visual information in real-time.
Tweets and Quotes from Influencers
Elon Musk (@elonmusk): “Our progress in self-driving technology is truly remarkable. Image recognition is the key to making autonomous vehicles a reality. #Tesla #AI”
Andrew Ng (@AndrewYNg): “Image recognition is revolutionizing multiple industries, from healthcare to retail. Excited about the future possibilities! #AI #DeepLearning”
Fei-Fei Li (@drfeifei): “AI and image recognition are transforming how we interact with the world. It’s a thrilling time to be in this field. #ComputerVision #AI”
Overcoming Challenges
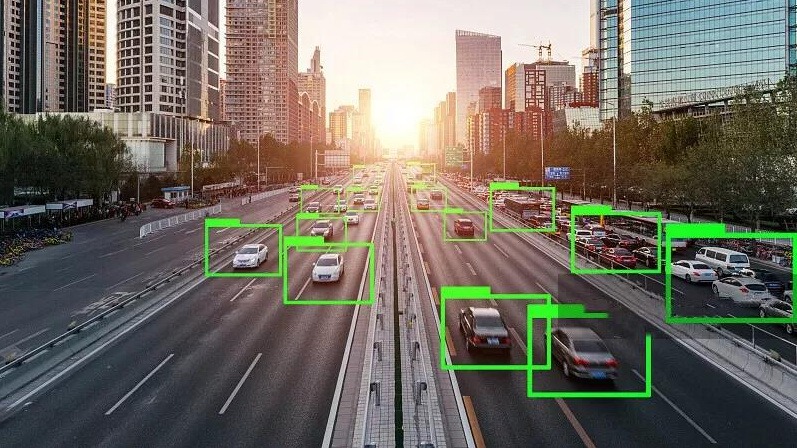
While image detection has made significant strides, several challenges persist:
1. Variability and Ambiguity
Images can exhibit significant variability and ambiguity due to differences in lighting conditions, viewpoints, occlusions, and object detection models. Teaching machines to recognize objects accurately under such circumstances remains a challenge.
2. Computational Complexity
Computer vision image recognition algorithms often require substantial computational resources and processing power to analyze large datasets efficiently. Balancing accuracy and computational efficiency is crucial, especially in real-time applications.
3. Training Data Limitations
Training image detection models require large and diverse datasets. Obtaining annotated data can be time-consuming and expensive, limiting the availability of quality training image data, especially for niche or specialized domains.
4. Ethical Considerations
As AI image recognition becomes more pervasive, ethical concerns arise. Issues like privacy, bias, and misuse of surveillance systems need to be addressed to ensure responsible deployment and use of this technology.
Future Trends
The future of image detection is promising, with ongoing advancements and research in the field. Improved algorithms, more extensive training datasets, and hardware innovations will contribute to even greater accuracy and efficiency. Image recognition will continue to shape industries, transform user experiences, and unlock new opportunities across diverse domains.
Conclusion
Image detection has emerged as a game-changing technology with wide-ranging applications. By enabling machines to interpret visual data, it empowers industries to automate processes, enhance security, improve healthcare diagnostics, and revolutionize the way we interact with technology. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and ethical considerations will pave the way for a future where image recognition becomes an integral part of our daily lives.
To experience the power of image recognition firsthand and discover how it can benefit your business, request a demo from AIM Technologies today. Our team of experts is ready to showcase the capabilities of our advanced image recognition solutions and assist you in harnessing their full potential.
FAQs
How does image recognition work?
- Image recognition works by utilizing complex algorithms and deep learning techniques to analyze visual data, extract meaningful features, and classify images based on the learned patterns.
Is image detection only limited to photographs?
- No, image detection can be applied to various forms of visual data, including photographs, video frames, satellite imagery, and medical scans.
Can image detection be used in art and design?
- Yes, image detection has applications in art and design, enabling tasks such as image restoration, and style transfer.
Are there any privacy concerns associated with image detection?
- Yes, privacy concerns arise with the increasing use of image detection technology, particularly in surveillance systems. Safeguards and regulations must be in place to protect individuals’ privacy rights.
How accurate is image detection technology?
- The accuracy of image detection technology depends on various factors, including the quality of training data, algorithm complexity, and the specific application. With advancements in deep learning, state-of-the-art models can achieve remarkable accuracy rates.